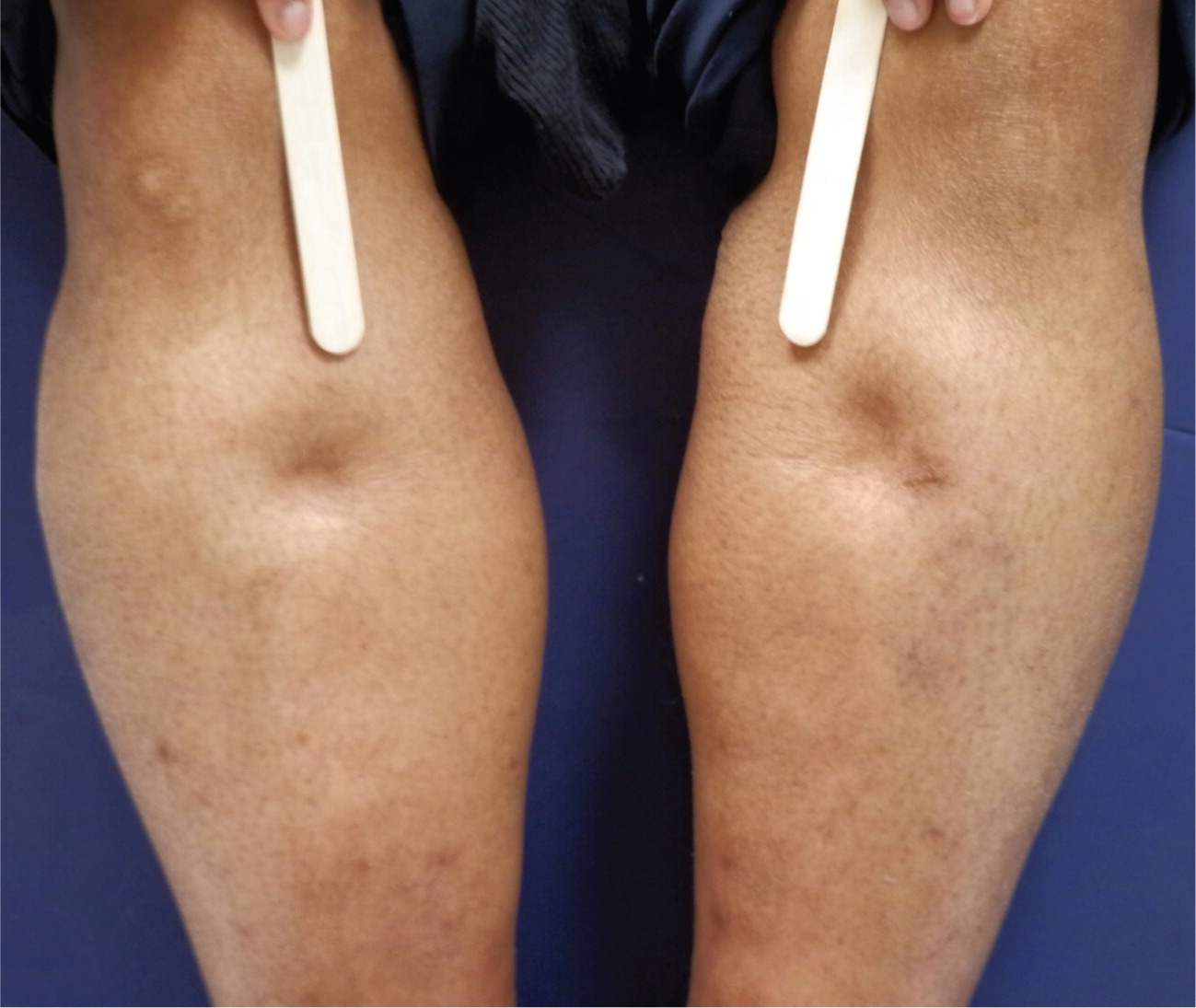
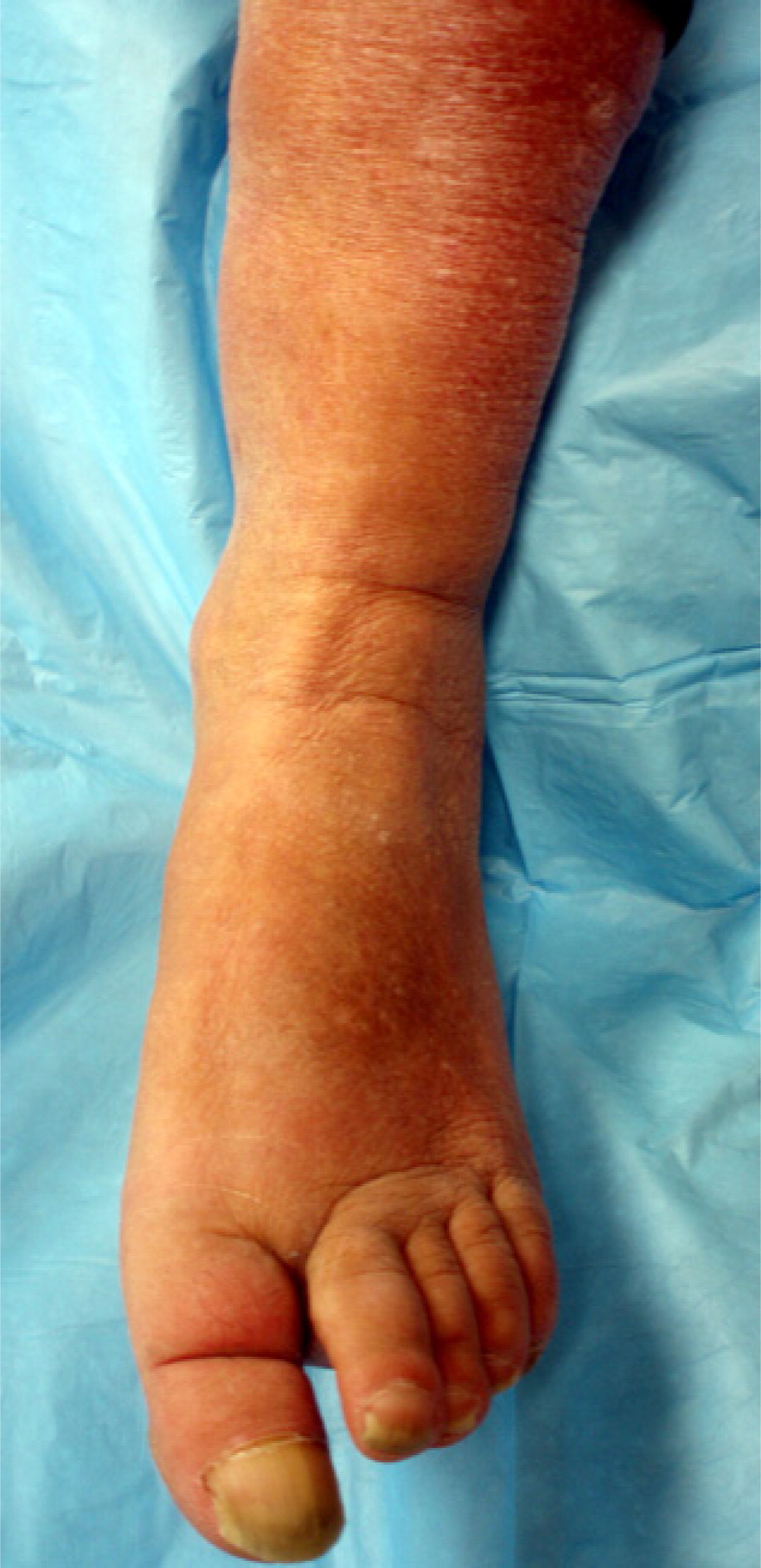
The history should include the timing of the edema, whether it changes with position, and if it is unilateral or bilateral, as well as a medication history and an assessment for systemic diseases (Table 2). Acute swelling of a limb over a period of less than 72 hours is more characteristic of deep venous thrombosis (DVT), cellulitis, ruptured popliteal cyst, acute compartment syndrome from trauma, or recent initiation of calcium channel blockers (Figures 1 and 2). The chronic accumulation of more generalized edema is due to the onset or exacerbation of chronic systemic conditions, such as congestive heart failure (CHF), renal disease, or hepatic disease. 4 , 5
Dependent edema caused by venous insufficiency is more likely to improve with elevation and worsen with dependency. 5 , 14 Edema associated with decreased plasma oncotic pressure (e.g., malabsorption, liver failure, nephrotic syndrome) does not change with dependency.
Unilateral swelling from compression or compromise of venous or lymphatic drainage can result from DVT, venous insufficiency, venous obstruction by tumor (e.g., tumor obstruction of the iliac vein), lymphatic obstruction (e.g., from a pelvic tumor or lymphoma), or lymphatic destruction (e.g., congenital vs. secondary from a tumor, radiation, or filariasis). Bilateral or generalized swelling suggests a systemic cause, such as CHF (especially right-sided), pulmonary hypertension, chronic renal or hepatic disease (causing hypoalbuminemia), protein-losing enteropathies, or severe malnutrition. 1 , 4 , 5
Edema can be an adverse effect of certain medications (Table 3 1 – 5 ). The mechanism often includes the retention of salt and water with increased capillary hydrostatic pressure. Diuretic use may cause volume depletion and reflex stimulation of the reninangiotensin system.
| Class | Specific medications |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, trazodone |
| Antihypertensives | Beta-adrenergic blockers, calcium channel blockers, clonidine (Catapres), hydralazine, methyldopa, minoxidil |
| Antivirals | Acyclovir (Zovirax) |
| Chemotherapeutics | Cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine (Sandimmune), cytosine arabinoside, mithramycin |
| Cytokines | Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interferon alfa, interleukin-2, interleukin-4 |
| Hormones | Androgen, corticosteroids, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone |
| Nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory drugs | Celecoxib (Celebrex), ibuprofen |
The history should also include questions about cardiac, renal, thyroid, or hepatic disease. Graves disease can lead to pretibial myxedema, whereas hypothyroidism can cause generalized myxedema. Although considered a diagnosis of exclusion, obstructive sleep apnea has been shown to cause edema. One study evaluated the apnea-hypopnea index in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and found that even when adjusted for age, body mass index, and the presence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus, the index was higher in patients who had edema. 15
The physical examination should assess for systemic causes of edema, such as heart failure (e.g., jugular venous distention, crackles), renal disease (e.g., proteinuria, oliguria), hepatic disease (e.g., jaundice, ascites, asterixis), or thyroid disease (e.g., exophthalmos, tremor, weight loss). Edema should also be evaluated for pitting, tenderness, and skin changes.
Pitting describes an indentation that remains in the edematous area after pressure is applied (Figure 3). This occurs when fluid in the interstitial space has a low concentration of protein, which is associated with decreased plasma oncotic pressure and disorders caused by increased capillary pressure (e.g., DVT, CHF, iliac vein compression). 4 , 16 The physician should describe the location, timing, and extent of the pitting to determine treatment response. Lower extremity examination should focus on the medial malleolus, the bony portion of the tibia, and the dorsum of the foot. Pitting edema also occurs in the early stages of lymphedema because of an influx of protein-rich fluid into the interstitium, before fibrosis of the subcutaneous tissue; therefore, its presence should not exclude the diagnosis of lymphedema. 6 , 7 Tenderness to palpation over the edematous area is associated with DVT and complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (i.e., reflex sympathetic dystrophy). Conversely, lymphedema generally does not elicit pain with palpation.

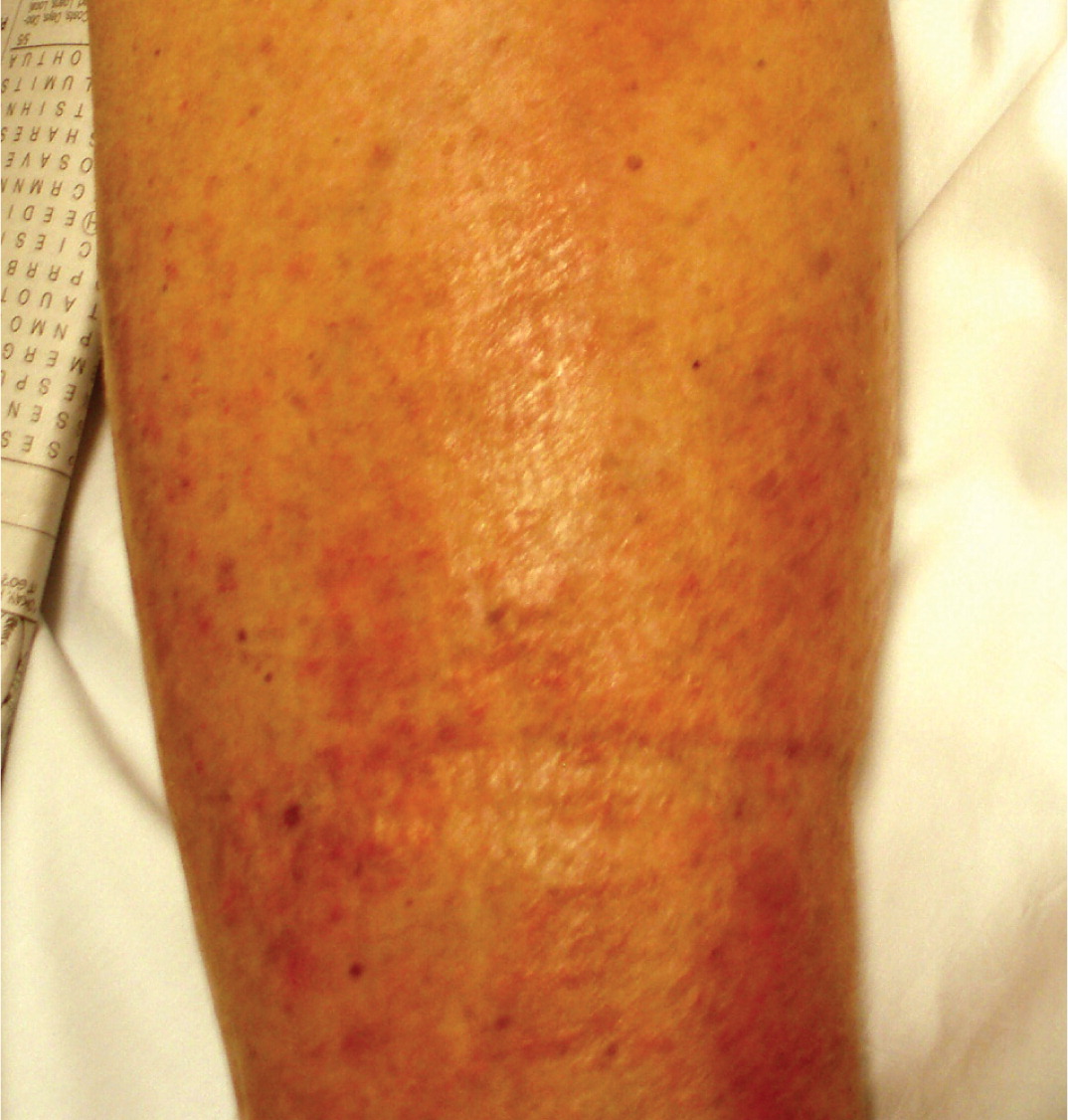
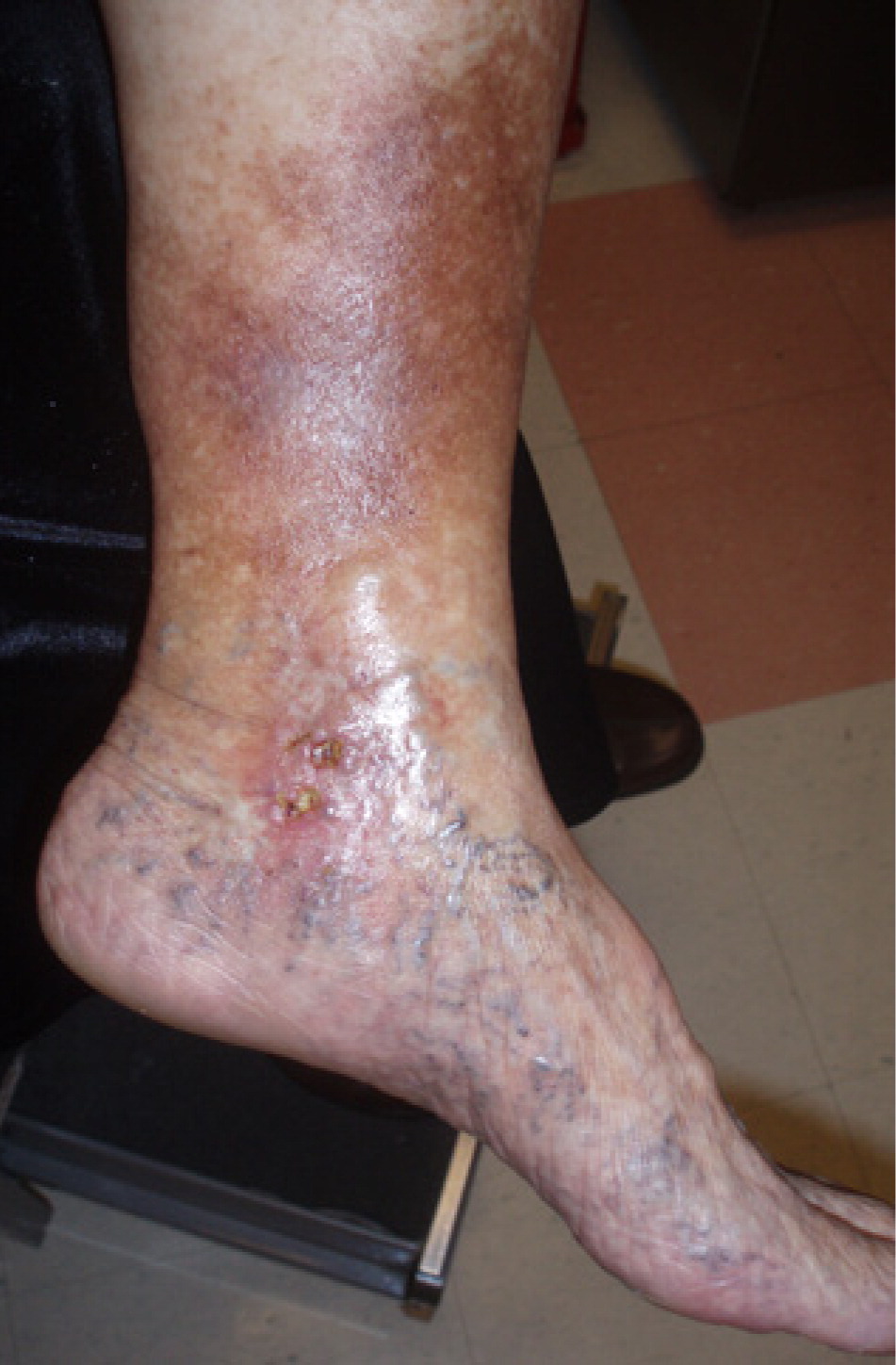
Changes in skin temperature, color, and texture provide clues to the cause of edema. For example, acute DVT and cellulitis (Figure 4) may produce increased warmth over the affected area. Because of the deposition of hemosiderin, chronic venous insufficiency is often associated with skin that has a brawny, reddish hue and commonly involves the medial malleolus 4 , 5 , 8 (eFigure A). As venous insufficiency progresses, it can result in lipodermatosclerosis (Figure 5), which is associated with marked sclerotic and hyperpigmented tissue, and characterized by fibrosis and hemosiderin deposition that can lead to venous ulcers over the medial malleolus. These ulcers may progress to deep, weeping erosions. Myxedema from hypothyroidism presents with a generalized dry, thick skin with nonpitting periorbital edema and yellow to orange skin discoloration over the knees, elbows, palms, and soles. Localized pretibial myxedema may be caused by Graves disease (eFigure B). In the late stages of complex regional pain syndrome, the skin may appear shiny with atrophic changes. In the early stages of lymphedema, the skin has a doughy appearance, whereas in the later stages, it becomes fibrotic, thickened, and verrucous (eFigure C).
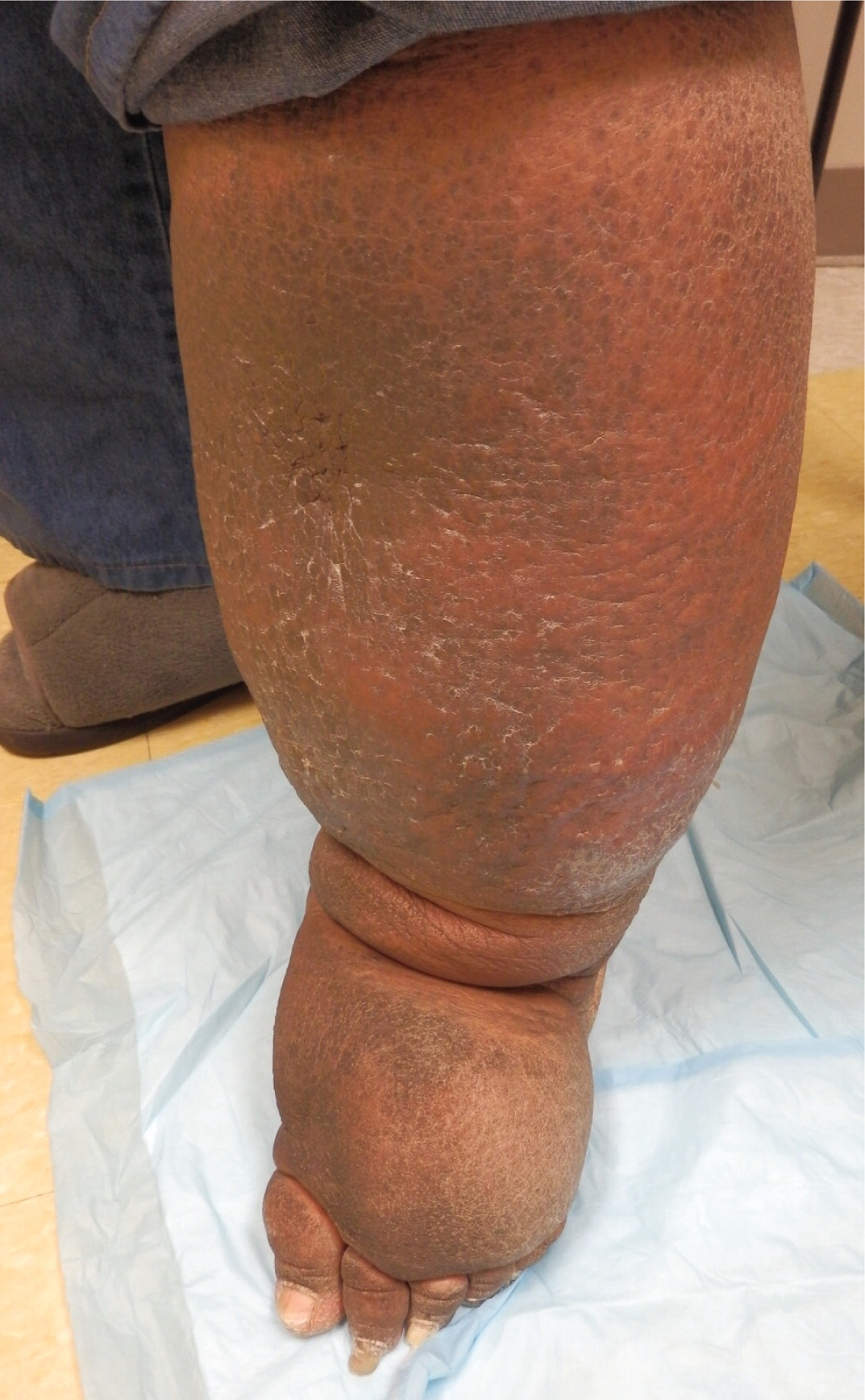
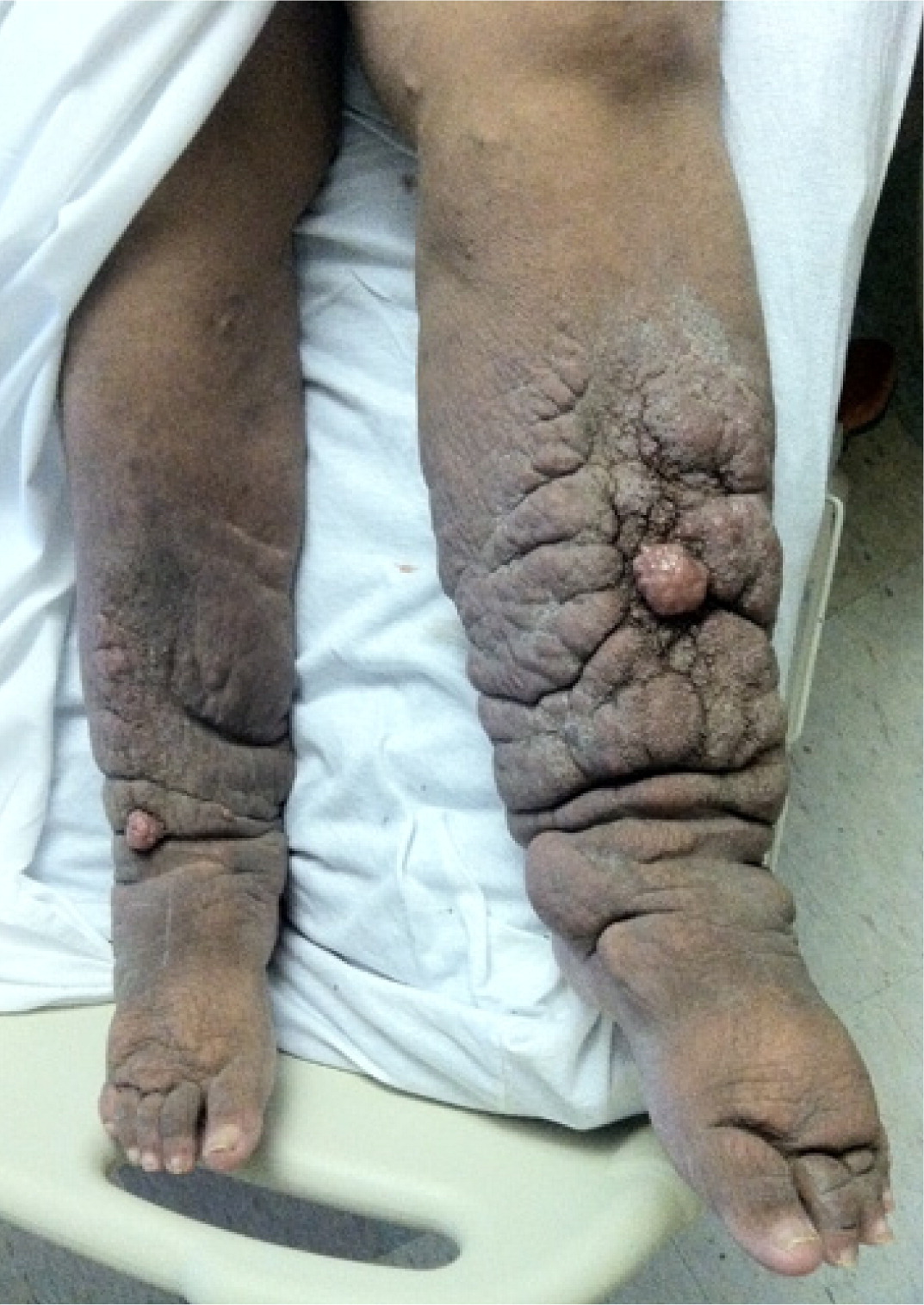
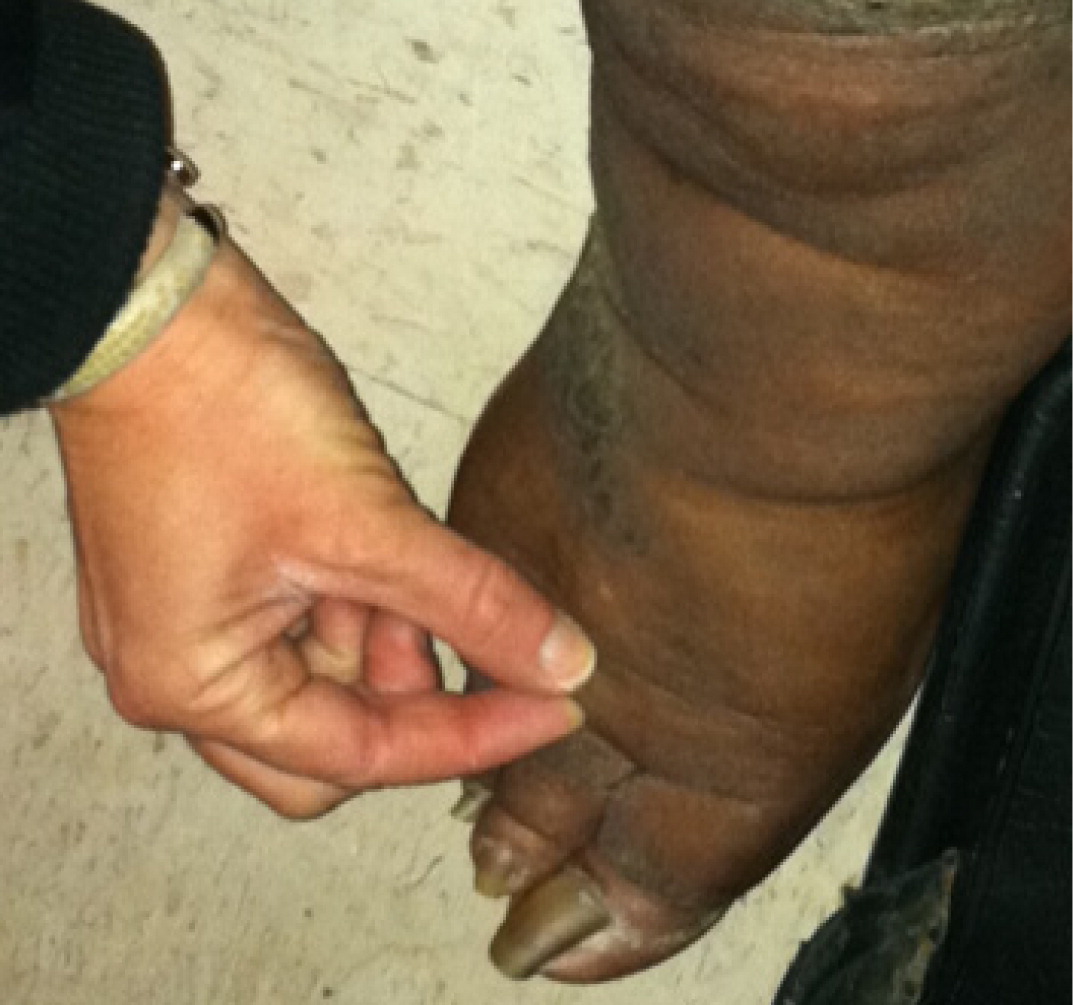
Examination of the feet is important in lower extremity edema. In patients with lymphedema, there is an inability to tent the skin of the dorsum of the second toe using a pincer grasp (Kaposi-Stemmer sign) 7 , 9 – 11 (eFigure D). In patients with lipedema, which is a pathologic accumulation of adipose tissue in the extremities, the feet are generally spared, although the ankles often have prominent malleolar fat pads. 12 Lipedema can also involve the upper extremities.
Recommendations for diagnostic testing are listed in Table 2. The following laboratory tests are useful for diagnosing systemic causes of edema: brain natriuretic peptide measurement (for CHF), creatinine measurement and urinalysis (for renal disease), and hepatic enzyme and albumin measurement (for hepatic disease). In patients who present with acute onset of unilateral upper or lower extremity swelling, a d-dimer enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay can rule out DVT in low-risk patients. However, this test has a low specificity, and d-dimer concentrations may be elevated in the absence of thrombosis. 13 , 17 , 18
Venous ultrasonography is the imaging modality of choice in the evaluation of suspected DVT. Compression ultrasonography with or without Doppler waveform analysis has a high sensitivity (95%) and specificity (96%) for proximal thrombosis; however, the sensitivity is lower for calf veins (73%). 13 , 19 , 20 Duplex ultrasonography can also be used to confirm the diagnosis of chronic venous insufficiency.
Lymph flow cannot be detected with ultrasonography. Therefore, indirect radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy, which shows absent or delayed filling of lymphatic channels, is the method of choice for evaluating lymphedema when the diagnosis cannot be made clinically. 11 , 21
Patients with unilateral lower extremity edema who do not demonstrate a proximal thrombosis on duplex ultrasonography may require additional imaging to diagnose the cause of edema if clinical suspicion for DVT remains high. Magnetic resonance angiography with venography of the lower extremity and pelvis can be used to evaluate for intrinsic or extrinsic pelvic or thigh DVT. 22 , 23 Compression of the left iliac vein by the right iliac artery (May-Thurner syndrome) should be suspected in women between 18 and 30 years of age who present with edema of the left lower extremity. 24 , 25 Magnetic resonance imaging may aid in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal etiologies, such as a gastrocnemius tear or popliteal cyst. T1-weighted magnetic resonance lymphangiography can be used to directly visualize the lymphatic channels when lymphedema is suspected. 7 , 11 , 26
Echocardiography to evaluate pulmonary arterial pressures is recommended for patients with obstructive sleep apnea and edema. 27 , 28 In one study of patients with obstructive sleep apnea, 93% of those with edema had elevated right arterial pressures. 27 Pulmonary hypertension has long been thought to be the cause of edema associated with obstructive sleep apnea. However, one study found that although a high proportion of patients with edema had obstructive sleep apnea (more than two-thirds), nearly one-third of these patients did not have pulmonary hypertension, which suggests a stronger correlation between edema and obstructive sleep apnea than can be explained by the presence of pulmonary hypertension alone. 28
Management of edema should be guided by the underlying etiology, which commonly includes chronic venous insufficiency, lymphedema, DVT, and medication-induced edema, among others (Table 2).
In patients with chronic venous insufficiency, diuretic therapy should be avoided unless a comorbid condition requires it (e.g., CHF). Mechanical therapies, including leg elevation and compression stockings with 20 to 30 mm Hg for mild edema and 30 to 40 mm Hg for severe edema complicated by ulceration, are recommended. 1 , 4 , 5 , 8 , 29 Compression therapy is contraindicated in patients with peripheral arterial disease. A study of 120 patients with venous ulcers showed that 6% had mixed arterial-venous ulcers. 30 In another study, a higher prevalence of peripheral arterial disease was found in women with symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency vs. those without symptoms. 31 Thus, measurement of ankle-brachial index should be considered in patients with risk factors for peripheral arterial disease before prescribing compression therapy.
Mixed evidence exists for the use of pneumatic compression devices in patients with chronic venous insufficiency. 29 , 32 However, these devices should be considered for patients in whom compression stockings are contraindicated. For mild to moderate chronic venous insufficiency, oral horse chestnut seed extract may be an alternative or adjunctive treatment to compression therapy. 33 , 34
Local skin and wound care of venous ulcers is essential in preventing secondary cellulitis and dermatitis. Eczematous (stasis) dermatitis, characterized by dry, inflamed, scaling skin overlying superficial varicose veins, often occurs in patients with chronic venous insufficiency. 35 Treatment includes daily hydration with emollients and short courses of topical steroid creams for severely inflamed skin. 36
The mainstay of lymphedema treatment involves complex decongestive physiotherapy, which is composed of manual lymphatic massage and multilayer bandages. The initial goal is to improve fluid resorption until a maximum therapeutic response is reached. The maintenance phase of treatment includes compression stockings at 30 to 40 mm Hg. 11 , 37 , 38 Pneumatic compression devices have been shown to augment standard therapies. One randomized controlled trial of women with breast cancer–related lymphedema showed statistically significant improvement in lymphatic function following one hour of pneumatic compression therapy. 39 In a study of 155 patients with cancer- and non–cancer-related lymphedema, 95% of patients noted reduction in limb edema after using pneumatic compression devices at home. 40 Surgical debulking or bypass procedures are limited to severe refractory cases. 7 Diuretics do not have a role in the treatment of lymphedema.
Acute thrombotic events are treated with anticoagulation therapy (unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin or warfarin [Coumadin]) to prevent progression of a clot or the development of postthrombotic syndrome. 13 Postthrombotic syndrome is characterized by chronic leg swelling, pain, cramping, and skin changes including telangiectasias, which occur in 20% to 50% of patients within five years of a thrombotic event. 41 – 43 In addition to anticoagulation, compression stockings should be used after a DVT to prevent postthrombotic syndrome. In a Cochrane review of two randomized controlled trials comparing elastic compression stockings (20 to 30 mm Hg) with placebo in patients with DVT, those who wore compression stockings had a statistically significant reduction in the risk of developing postthrombotic syndrome (odds ratio = 0.39; 95% confidence interval, 0.20 to 0.76) after two years. 41 A randomized controlled trial of 209 patients with proximal DVT showed that those who received catheter-directed thrombolysis in addition to conservative therapy with compression stockings and anticoagulation had a lower prevalence of postthrombotic syndrome after 24 months compared with conservative therapy alone, suggesting that thrombolysis may be a treatment option for select patients. 44
In patients with suspected medication-induced edema, the offending medication should be discontinued if possible. In patients taking calcium channel blockers to treat hypertension, use of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor may be more beneficial than angiotensin receptor blocker therapy in reducing calcium channel blocker–induced peripheral edema. 45 , 46
There is no treatment for lipedema. Weight loss does not affect this condition. Complex regional pain syndrome is treated with physical therapy in combination with medications such as systemic steroids and tricyclic antidepressants. 47 Obstructive sleep apnea is treated with positive pressure ventilation. 48
Data Sources: A PubMed search was performed for clinical reviews, randomized controlled trials, and meta-analyses. Key search terms were edema, oedema, peripheral edema, lower extremity edema, venous insufficiency, deep vein thrombosis, lymphedema, obstructive sleep apnea, and iliac vein syndrome. Also reviewed were the Cochrane database, National Guideline Clearinghouse, Essential Evidence Plus, UpToDate, and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force website. Search date: January 2012.